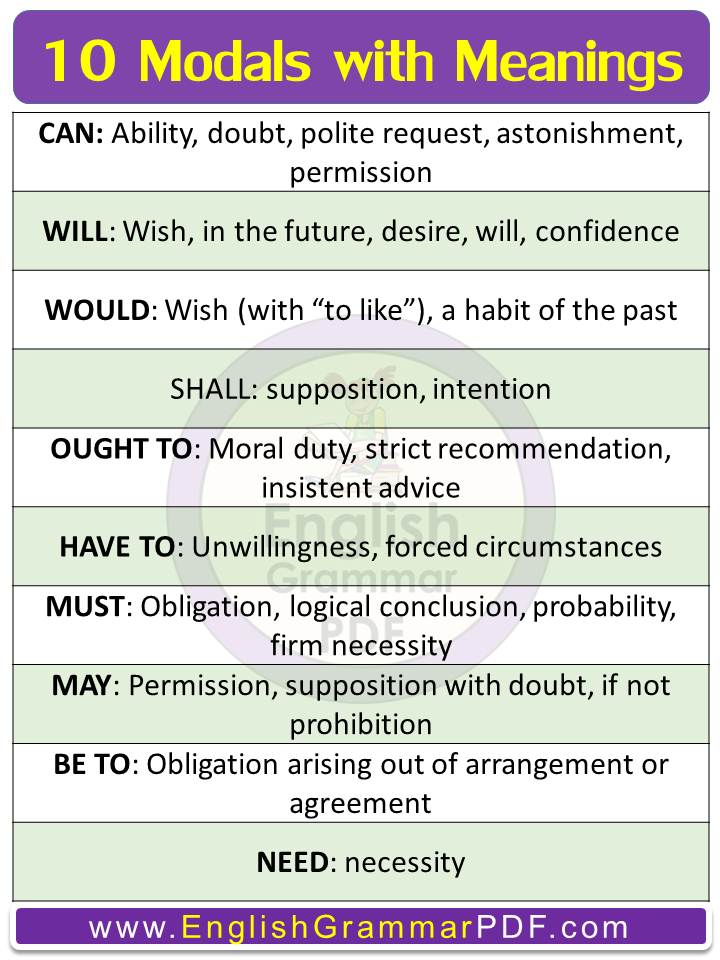
Modals are special helping words we use to express things like ability, possibility, permission, or obligation. Imagine them as little helpers that change the meaning of the main verb in a sentence to tell us more about what’s happening.
They’re like the secret sauce that adds flavor to your sentences, making them richer and more informative. Whether you’re just starting to learn English or looking to polish your skills, understanding modals is a big step forward. This blog post will introduce you to 10 common modals with clear examples, making it easier for you to use them in your everyday conversations.
You may like to read: 75 writing verbs
10 Examples of Modals
1. CAN:
-
- Ability: “She can solve complex math problems effortlessly.”
- Doubt: “Can it really be that late already?”
- Polite Request: “Can you please pass the salt?”
- Astonishment: “Can you believe he won the lottery?”
- Permission: “Can I leave the table now, Mom?”
2. WILL:
-
- Wish: “I will for a peaceful resolution to the conflict.”
- In the Future: “It will rain tomorrow according to the weather forecast.”
- Desire: “I will have a cup of coffee, please.”
- Will: “I will finish this project by tomorrow, no matter what.”
- Confidence: “Don’t worry, you will do great on your test.”
3. WOULD:
-
- Wish (with “to like”): “I would like to visit Japan someday.”
4. SHALL:
-
- Supposition: “Shall we expect you at dinner?”
- Intention: “I shall complete the report by this evening.”
5. OUGHT TO:
-
- Moral Duty: “You ought to apologize for your mistake.”
- Strict Recommendation: “You ought to see a doctor about that cough.”
- Insistent Advice: “You really ought to start saving for retirement.”
6. HAVE TO:
-
- Unwillingness: “I have to work late tonight, unfortunately.”
- Forced Circumstances: “We have to evacuate the building due to the fire alarm.”
7. MUST:
-
- Obligation: “You must wear a helmet when riding a motorcycle.”
- Logical Conclusion: “If the street is wet, it must have rained last night.”
- Probability: “She must be at home; her car is in the driveway.”
- Firm Necessity: “You must stop smoking for your health.”
8. MAY:
-
- Permission: “May I use your phone?”
- Supposition with Doubt: “There may be a strike next week.”
- If Not Prohibition: “You may enter the competition if you’re over 18.”
9. BE TO:
-
- Obligation Arising out of Arrangement or Agreement: “You are to finish this by tomorrow as per our agreement.”
10. NEED:
-
- Necessity: “You need to take your medicine to feel better.”
You can Download Pdf of this lesson.
DOWNLOAD PDF