The infinitive form of a verb, often recognized by the word “to” followed by the base form of the verb, is a versatile grammatical structure in English. Understanding when and how to use infinitives can significantly enhance your clarity and variety in writing and speaking. Here’s a detailed guide to help you master the correct use of infinitives.
Correct Use of Infinitive
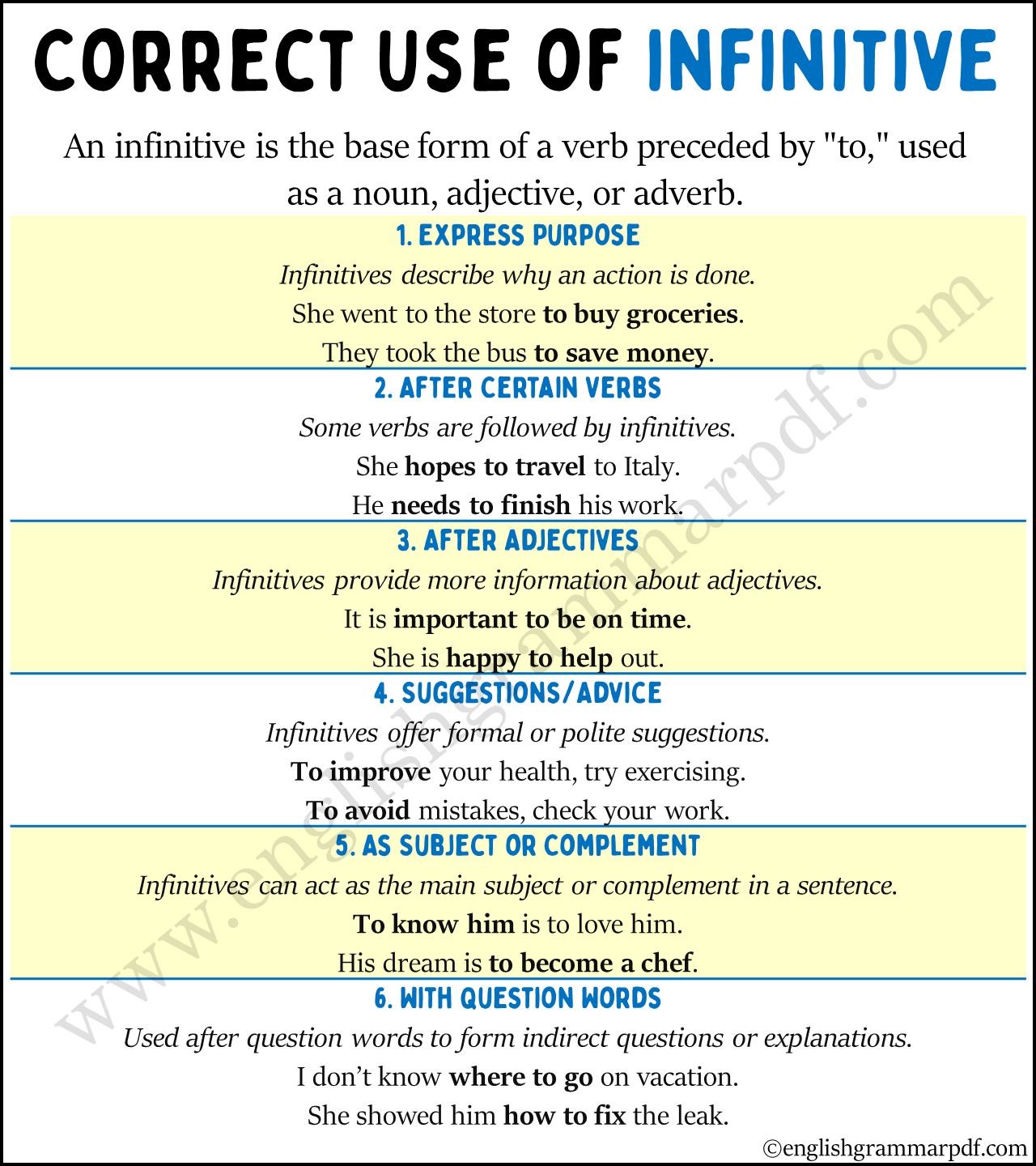
1. To Express Purpose
Infinitives are commonly used to explain the purpose of an action. This usage answers the question Why? something is done.
Examples:
- She went to the store to buy groceries.
- They took the bus to save money.
2. After Certain Verbs
Some verbs are usually followed by an infinitive. This includes verbs of decision, necessity, and desire.
Examples:
- She hopes to travel to Italy next summer.
- He needs to finish his work before the deadline.
3. After Adjectives
It is also common to use an infinitive after adjectives to give more information about the adjective.
Examples:
- It is important to be on time.
- She is happy to help out.
4. To Make Suggestions or Give Advice
Infinitives can be used to suggest or advise actions, often in a more formal or polite manner.
Examples:
- To improve your health, try exercising regularly.
- To avoid mistakes, check your work thoroughly.
5. As Subject or Complement
Infinitives can serve as the subject of a sentence or as a complement to the subject.
Examples:
- To know him is to love him.
- His dream is to become a chef.
6. With Question Words
Infinitives are used after question words to form indirect questions or to explain more about the question word.
Examples:
- I don’t know where to go on vacation.
- She showed him how to fix the leak.
7. Bare Infinitive (without ‘to’)
Certain situations call for using the bare infinitive (the infinitive without to), especially after modal verbs or certain other verbs like let, make, and help.
Examples:
- She can swim very fast.
- Let him know that we are here.
Conclusion
Infinitives are a fundamental part of English grammar that, when used effectively, can make your communication more precise and varied. They allow you to convey reasons, suggestions, and much more with elegance and clarity. Understanding their role and function within different contexts will greatly aid in your overall language proficiency.


