Gerunds, verb forms ending in -ing that function as nouns, are versatile components in English grammar. They can be tricky to master because their usage spans various grammatical structures. Here’s a detailed exploration of all the scenarios in which gerunds are used, helping you to navigate this complex topic.
Correct Use of Gerund
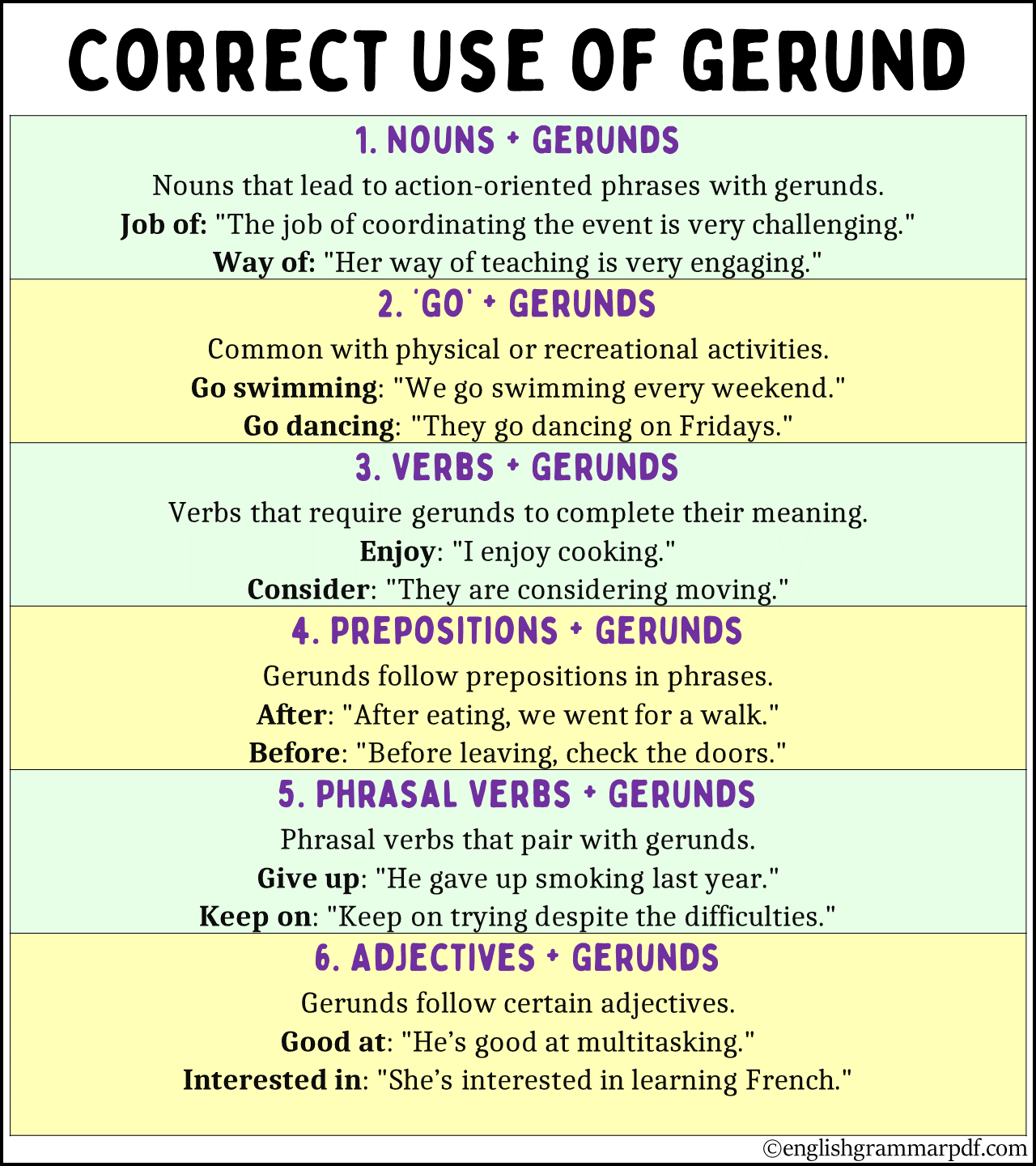
1. Verbs Followed by Gerunds
Certain verbs naturally take a gerund after them because they need an action to complete their meaning. These include:
- Enjoy: “I enjoy painting.”
- Avoid: “She avoids talking too much.”
- Consider: “They are considering relocating.”
2. Prepositions Before Gerunds
Prepositions are often followed by gerunds, as prepositions require a noun or something similar to complete the sentence:
- After: “After running, I like to cool down.”
- Before: “Before going out, she checks the weather.”
3. Phrasal Verbs Followed by Gerunds
Phrasal verbs that involve activities or actions often pair with gerunds:
- Give up: “He gave up smoking last year.”
- Keep on: “Keep on trying until you succeed.”
4. Expressions with Gerunds
Expressions implying necessity or futility frequently use gerunds:
- Can’t stand: “I can’t stand waiting in lines.”
- It’s no use: “It’s no use worrying about the past.”
5. After Certain Adjectives
Gerunds are used after adjectives to complete the meaning, particularly when the adjective describes an attitude towards an action:
- Good at: “He’s good at multitasking.”
- Interested in: “She’s interested in learning new languages.”
6. Nouns Followed by Gerunds
Nouns that are often part of phrases that describe activities will follow with a gerund:
- Job of: “The job of organizing the event is hers.”
- Way of: “Her way of dealing with stress is meditation.”
7. After ‘Go’ for Physical Activities
Using “go” with gerunds is common when referring to recreational activities:
- Go skiing: “We go skiing every winter.”
- Go dancing: “They go dancing on Fridays.”
8. After Preference Verbs
Preference verbs express likes, dislikes, or preferences and are followed by gerunds:
- Love: “I love reading.”
- Dislike: “He dislikes flying.”