In this blog post, we’re diving into the essential language tool of forming direct and indirect questions across various tenses. Understanding this distinction enhances your clarity and flexibility in everyday communication.
Direct and Indirect Questions
Direct questions are straightforward inquiries that require a response, characterized by their interrogative structure and punctuation, such as a question mark. Example: Where do you live?
Indirect questions, on the other hand, are embedded within statements or other questions, making them less direct and more polite. They do not end with a question mark in writing. Example: Could you tell me where you live?
Direct and Indirect Questions for All Tenses
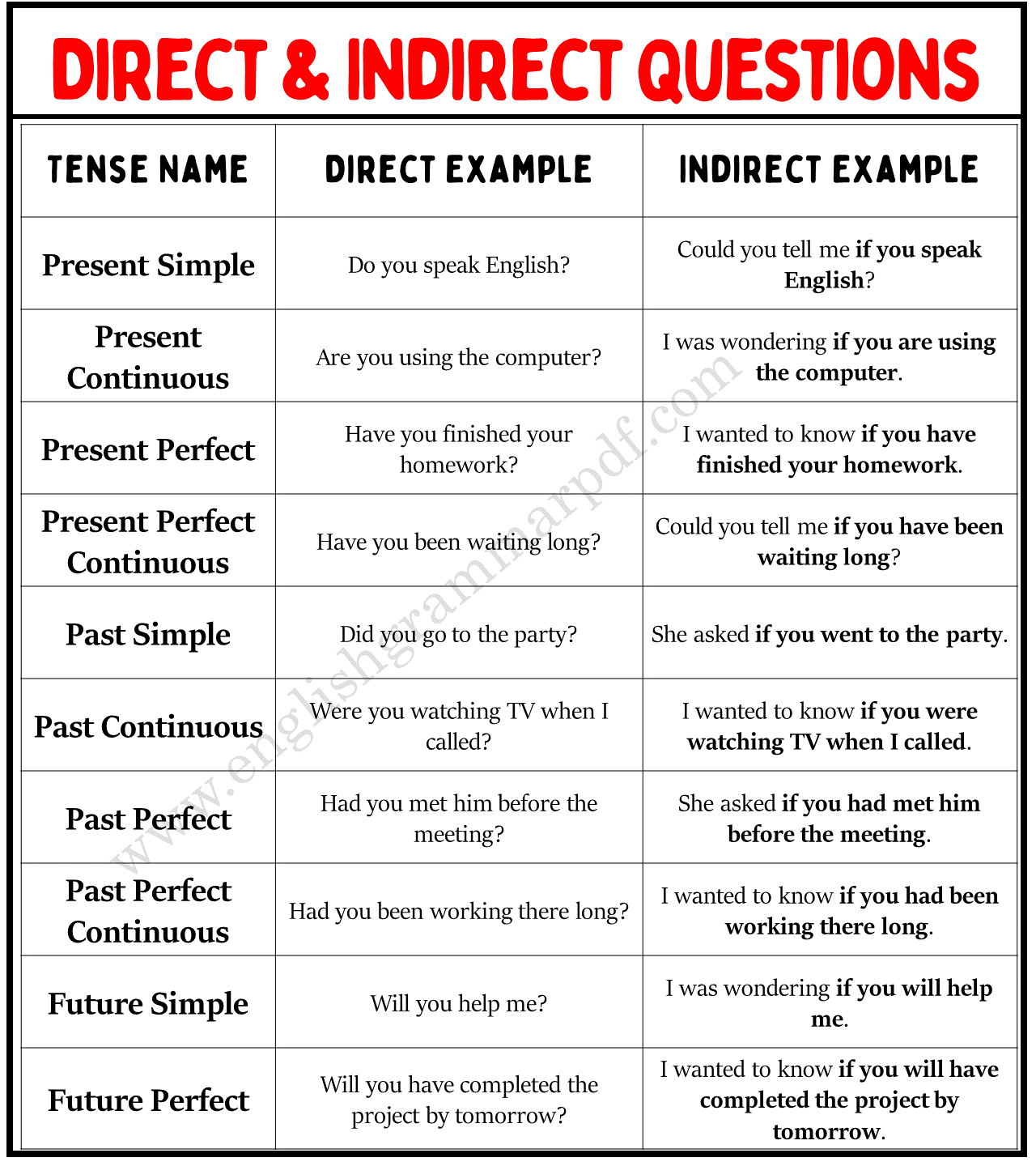
Present Simple
Rules for Indirect: Use a polite introductory phrase followed by ‘if’ or ‘whether’ for yes/no questions, and ‘wh-‘ words for open questions.
Examples:
- Direct: Do you speak English?
- Indirect: Could you tell me if you speak English?
- Direct: Where does he work?
- Indirect: Do you know where he works?
Present Continuous
Rules for Indirect: Start with a polite phrase, followed by the question using the present continuous form in indirect speech.
Examples:
- Direct: Are you using the computer?
- Indirect: I was wondering if you are using the computer.
- Direct: What are you doing?
- Indirect: Can you tell me what you are doing?
Present Perfect
Rules for Indirect: Begin with a polite expression, followed by ‘if’ or ‘whether’ for yes/no questions, and ‘wh-‘ words for open questions in the present perfect.
Examples:
- Direct: Have you finished your homework?
- Indirect: I wanted to know if you have finished your homework.
- Direct: Why has she left the room?
- Indirect: Can you explain why she has left the room?
Present Perfect Continuous
Rules for Indirect: Use a polite introductory phrase, followed by the question in the present perfect continuous form indirectly.
Examples:
- Direct: Have you been waiting long?
- Indirect: Could you tell me if you have been waiting long?
- Direct: What have you been doing?
- Indirect: I was wondering what you have been doing.
Past Simple
Rules for Indirect: Use a past tense verb in the introductory phrase, followed by ‘if’ or ‘whether’ for yes/no questions, and ‘wh-‘ words for open questions.
Examples:
- Direct: Did you go to the party?
- Indirect: She asked if you went to the party.
- Direct: Where did you buy this?
- Indirect: He wanted to know where you bought this.
Past Continuous
Rules for Indirect: Start with a past tense introductory phrase, followed by the past continuous form of the verb in the indirect question.
Examples:
- Direct: Were you watching TV when I called?
- Indirect: I wanted to know if you were watching TV when I called.
- Direct: What were they doing?
- Indirect: Could you tell me what they were doing?
Past Perfect
Rules for Indirect: Begin with a past tense introductory phrase, then frame the question using the past perfect tense.
Examples:
- Direct: Had you met him before the meeting?
- Indirect: She asked if you had met him before the meeting.
- Direct: Why had they left early?
- Indirect: He inquired why they had left early.
Past Perfect Continuous
Rules for Indirect: Use a past tense introductory phrase, followed by the question in the past perfect continuous form.
Examples:
- Direct: Had you been working there long?
- Indirect: I wanted to know if you had been working there long.
- Direct: What had you been doing?
- Indirect: Could you tell me what you had been doing?
Future Simple
Rules for Indirect: Begin with a modal or polite phrase, followed by ‘if’ or ‘whether’ for yes/no questions, and ‘wh-‘ words for open questions in the future tense.
Examples:
- Direct: Will you help me?
- Indirect: I was wondering if you will help me.
- Direct: When will you leave?
- Indirect: Can you tell me when you will leave?
Future Perfect
Rules for Indirect: Start with a polite phrase, then use the future perfect form of the verb in the indirect question.
Examples:
- Direct: Will you have completed the project by tomorrow?
- Indirect: I wanted to know if you will have completed the project by tomorrow.
- Direct: By when will they have arrived?
- Indirect: Can you tell me by when they will have arrived?
This structure ensures that each type of tense is adapted appropriately for indirect questions, maintaining both grammatical accuracy and politeness in communication.