In English, most words become plural by adding an “-s” or “-es” at the end, like “cats” or “buses.” But, some words don’t follow this rule and change in different ways. These are called irregular plurals. For example, “child” becomes “children,” not “childs.” This blog post will talk about these unusual words, helping English learners understand and remember them better. So, if you’re learning English or trying to improve, this is for you!
Rules to Make Irregular Plurals
Irregular plurals in English can seem tricky at first because they don’t follow the standard rules of adding “-s” or “-es” to make a noun plural. Instead, these words change in unique ways. Understanding the different patterns can help learners master these exceptions.
1. Vowel Changes
Some nouns change their internal vowel to form the plural. This is a throwback to old English and can be seen in words where the vowel in the middle of the word changes when it becomes plural.
- Example: “Man” becomes “Men,” and “Woman” becomes “Women.”
2. Words Ending in -f or -fe
For some nouns ending in “-f” or “-fe,” the plural form is made by changing “-f” or “-fe” to “-ves.”
- Example: “Knife” becomes “Knives,” and “Leaf” becomes “Leaves.”
However, be aware that there are exceptions to this rule, such as “roof” to “roofs.”
3. Irregular Endings
Some nouns have unique plural forms that don’t fit into common patterns and must be memorized.
- Example: “Child” becomes “Children,” “Person” becomes “People,” and “Mouse” becomes “Mice.”
4. Same Singular and Plural Forms
Some nouns have the same form in both singular and plural. These are often names of animals or other specific items.
- Example: “Sheep” remains “Sheep” whether it’s one or many, and the same goes for “Fish” (though “Fishes” can be used when referring to multiple species).
5. Foreign-Origin Words
English has borrowed words from many languages, keeping their original plural forms, especially from Latin and Greek. These plurals can seem quite irregular to those unfamiliar with the source languages.
- Latin Example: “Cactus” becomes “Cacti,” and “Datum” becomes “Data.”
- Greek Example: “Analysis” becomes “Analyses,” and “Crisis” becomes “Crises.”
Practice and Memorization
The key to mastering irregular plurals is exposure and practice. Reading, listening, and speaking English as much as possible can help you encounter these irregular forms in context, making them easier to remember. Additionally, practicing with exercises and flashcards can reinforce your knowledge and help you recall these irregular plurals when you need them.
Understanding the patterns can reduce the amount of memorization required, but due to the nature of irregular plurals, some degree of memorization will always be necessary. Don’t be discouraged by the exceptions; with time and practice, you’ll find that these irregularities become more familiar and less daunting.
Irregular Plurals Noun List
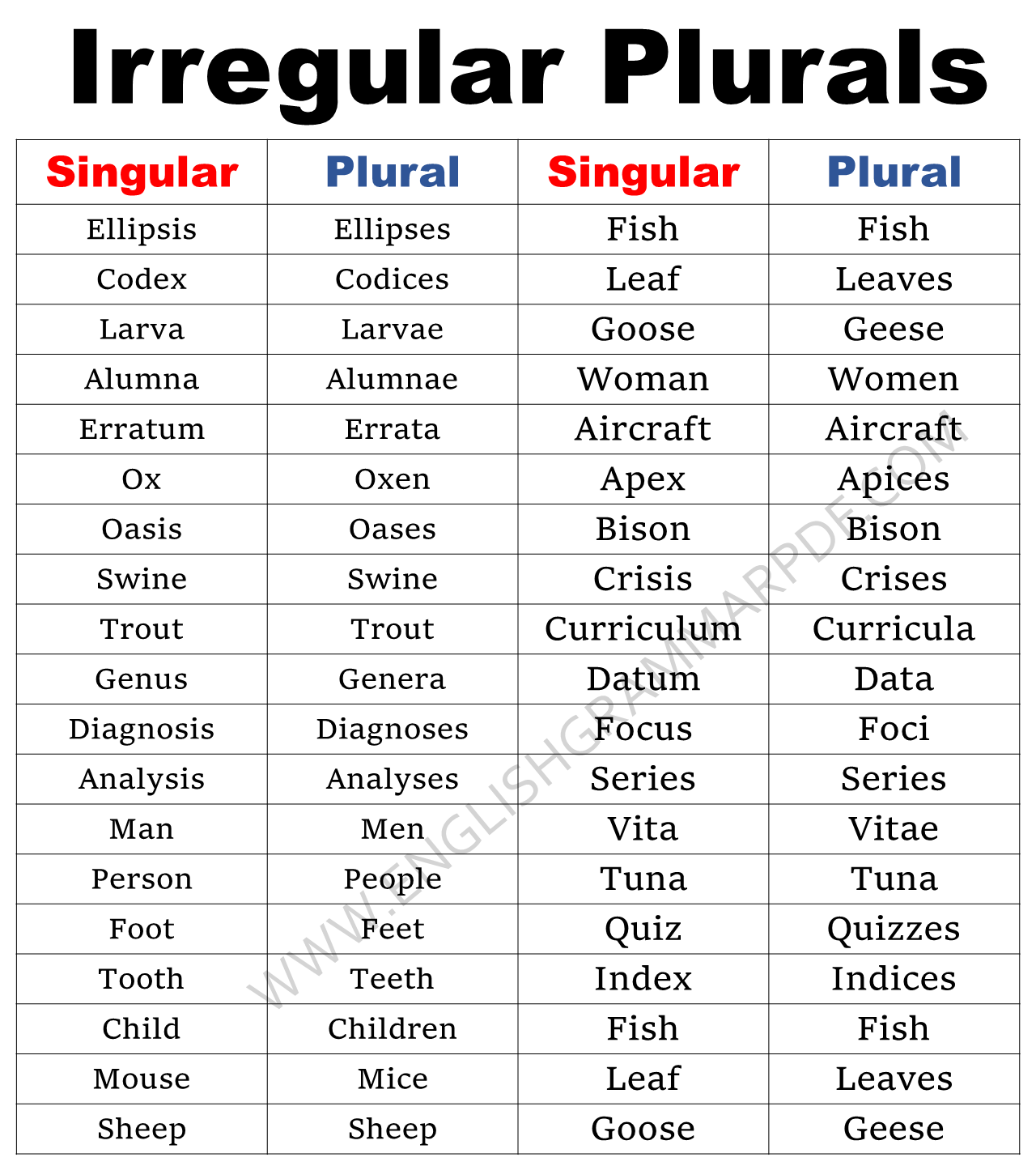
| Singular | Plural |
| Antenna | Antennae |
| Bison | Bison |
| Criterion | Criteria |
| Foot | Feet |
| Genus | Genera |
| Larva | Larvae |
| Leaf | Leaves |
| Nucleus | Nuclei |
| Ox | Oxen |
| Sheep | Sheep |
| Sheep | Sheep |
| Tooth | Teeth |
| Vita | Vitae |
| Alumnus | Alumni |
| Bacterium | Bacteria |
| Corpus | Corpora |
| Erratum | Errata |
| Erratum | Errata |
| Foot | feet |
| Grouse | Grouse |
| Leaf | Leaves |
| Mouse | Mice |
| Quiz | Quizzes |
| Synopsis | Synopses |
| Wife | Wives |
| Aircraft | Aircraft |
| Aircraft | Aircraft |
| Axis | Axes |
| Codex | Codices |
| Codex | Codies |
| Curriculum | Curricula |
| Diagnosis | Diagnoses |
| Goose | Geese |
| Man | Men |
| Phylum | Phyla |
| Series | Series |
| Swine | Swine |
| Woman | Women |
| Antithesis | Antitheses |
| Bureau | Bureaux |
| Curriculum | Curricula |
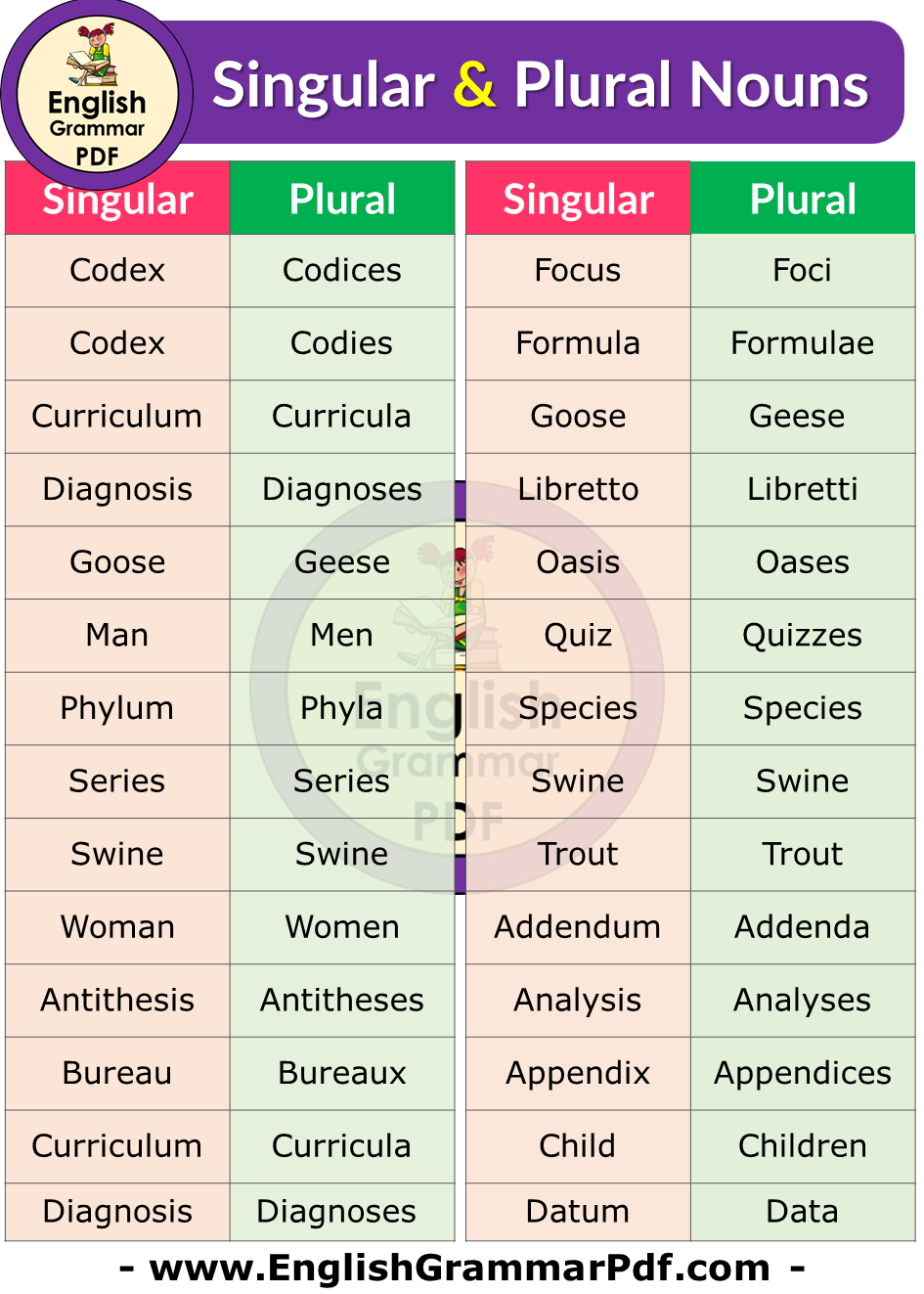
| Singular | Plural |
| Diagnosis | Diagnoses |
| Focus | Foci |
| Formula | Formulae |
| Goose | Geese |
| Libretto | Libretti |
| Oasis | Oases |
| Quiz | Quizzes |
| Species | Species |
| Swine | Swine |
| Trout | Trout |
| Addendum | Addenda |
| Analysis | Analyses |
| Appendix | Appendices |
| Child | Children |
| Datum | Data |
| Deer | Deer |
| Ellipsis | Ellipses |
| Genus | Genera |
| Louse | Lice |
| Ox | Oxen |
| Stratum | Strata |
| Tooth | Teeth |
| Vita | Vitae |
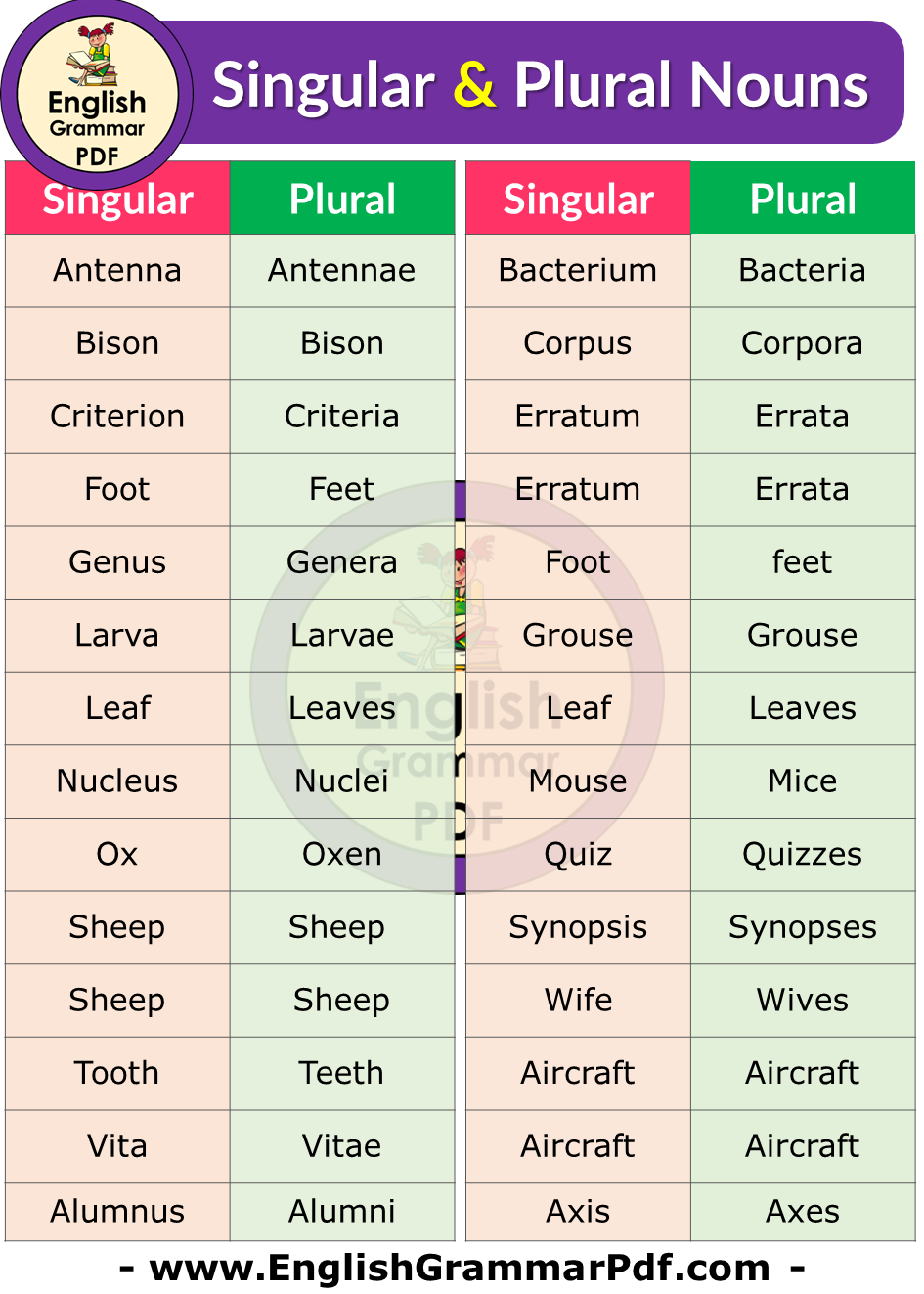
| Alumna | Alumnae |
| Apex | Apices |
| Cactus | Cacti |
| Datum | Data |
| Fungus | Fungi |
| Index | Indices |
| Locus | Loci |
| Ovum | Ova |
| Person | People |
| Stimulus | Stimuli |
| Trout | Trout |
| Tuna | Tuna |
| Tuna | Tuna |
| Analysis | Analyses |
| Basis | Bases |
| Crisis | Crises |
| Deer | Deer |
| Fish | Fish |
| Focus | Foci |
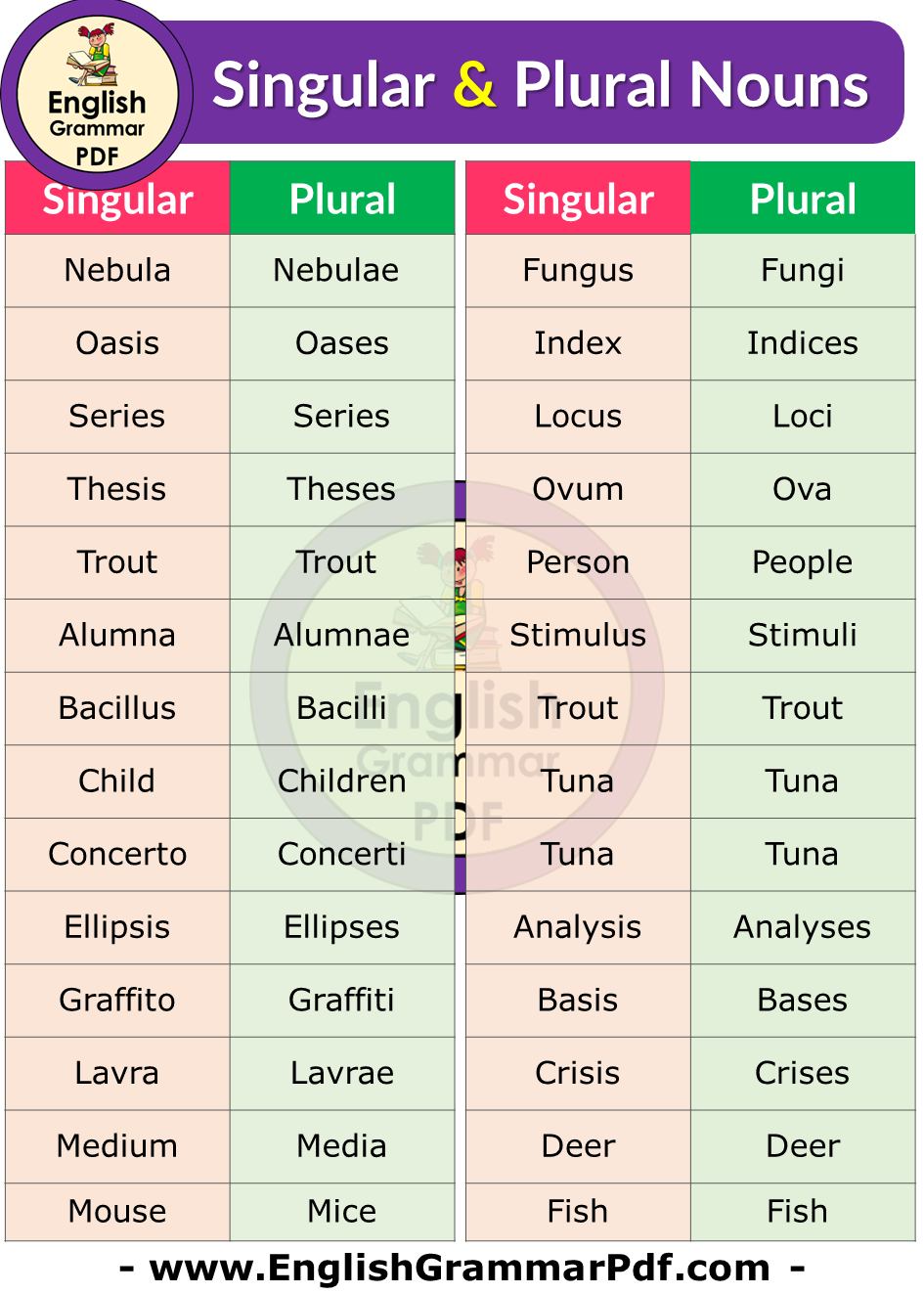
| Singular | Plural |
| Index | Indices |
| Nebula | Nebulae |
| Nebula | Nebulae |
| Oasis | Oases |
| Series | Series |
| Thesis | Theses |
| Trout | Trout |
| Alumna | Alumnae |
| Bacillus | Bacilli |
| Child | Children |
| Concerto | Concerti |
| Ellipsis | Ellipses |
| Graffito | Graffiti |
| Lavra | Lavrae |
| Medium | Media |
| Mouse | Mice |
| Prognosis | Prognoses |
| Syllabus | Syllabi |
| Woman | Women |
Download this Lesson in PDF