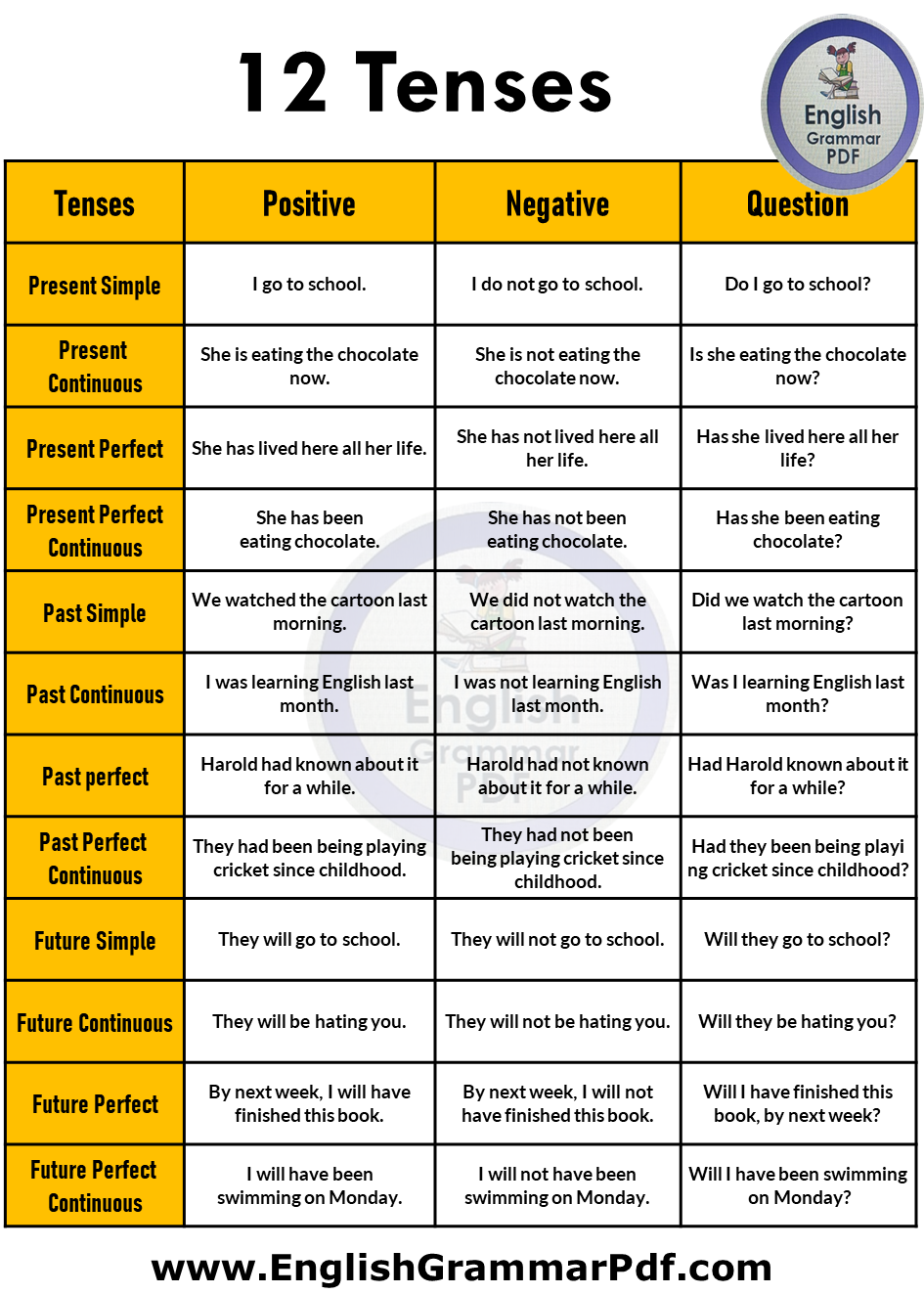
Understanding verb tenses is crucial for effective communication in any language. The tense chart provides a comprehensive overview of the different tenses, helping learners grasp the nuances of time and action within a sentence. By examining the structures and examples of each tense, learners can appreciate the precise ways in which verbs express when an action occurs.
This insight enables them to communicate with accuracy and clarity, enhancing their overall language proficiency. The tense chart also reveals how various tenses interact with each other within a narrative or conversation, shedding light on the subtleties of expressing past, present, and future events.
Rather than viewing tenses as rigid categories, this exploration allows for a more dynamic understanding that considers context and intention. Through studying this chart, learners gain practical tools for effectively conveying actions to time, further empowering them to engage in meaningful communication across diverse contexts and settings.
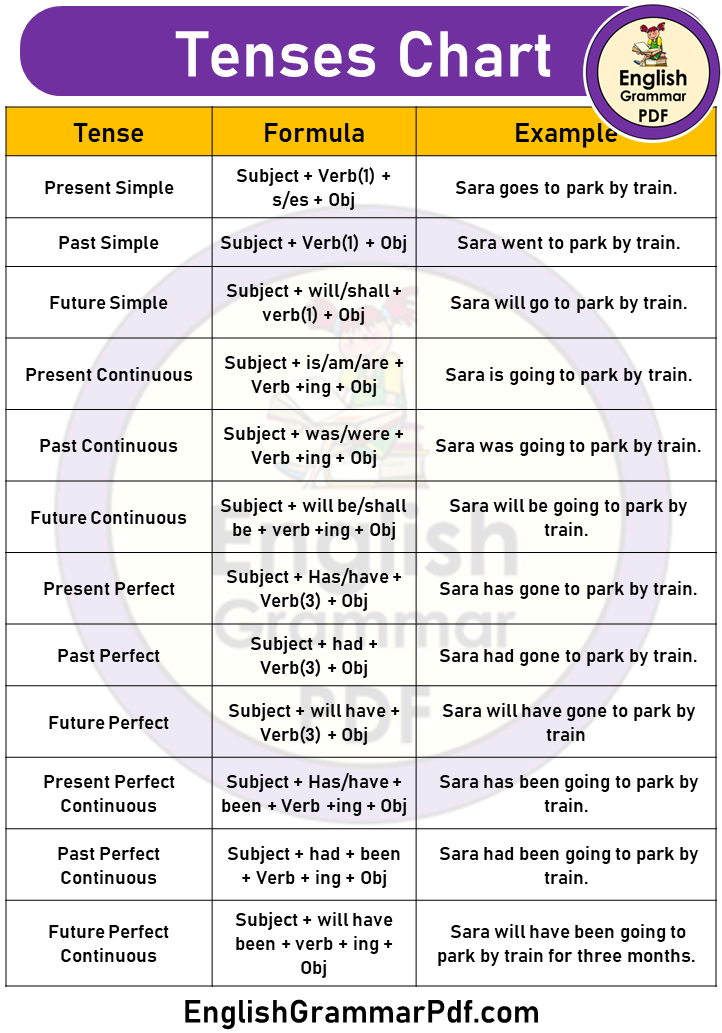
12 Tenses Chart
Here is the chart of all tenses in English Grammar;
| Tenses | Formula | Example |
| 1. Present Simple | Subject + Verb(1) + s/es + Obj | Sara goes to the park by train. |
| 2. Past Simple | Subject + Verb(1) + Obj | Sara went to the park by train. |
| 3. Future Simple | Subject + will/shall + verb(1) + Obj | Sara will go to the park by train. |
| 4. Present Continuous | Subject + is/am/are + Verb +ing + Obj | Sara is going to the park by train. |
| 5. Past Continuous | Subject + was/were + Verb +ing + Obj | Sara was going to the park by train. |
| 6. Future Continuous | Subject + will be/shall be + verb +ing + Obj | Sara will be going to the park by train. |
| 7. Present Perfect | Subject + Has/have + Verb(3) + Obj | Sara has gone to the park by train. |
| 8. Past Perfect | Subject + had + Verb(3) + Obj | Sara had gone to park by train. |
| 9. Future Perfect | Subject + will have + Verb(3) + Obj | Sara will have gone the park by train |
| 10. Present Perfect Continuous | Subject + Has/have + been + Verb +ing + Obj | Sara has been going to park by train. |
| 11. Past Perfect Continuous | Subject + had + been + Verb + ing + Obj | Sara had been going to park by train. |
| 12. Future Perfect Continuous | Subject + will have been + verb + ing + Obj | Sara will have been going to the park by train for three months. |
[DOWNLOAD PDF] of all 12 Tenses Chart with Definitions, Formation, and Examples.
What are the 12 types of tenses?
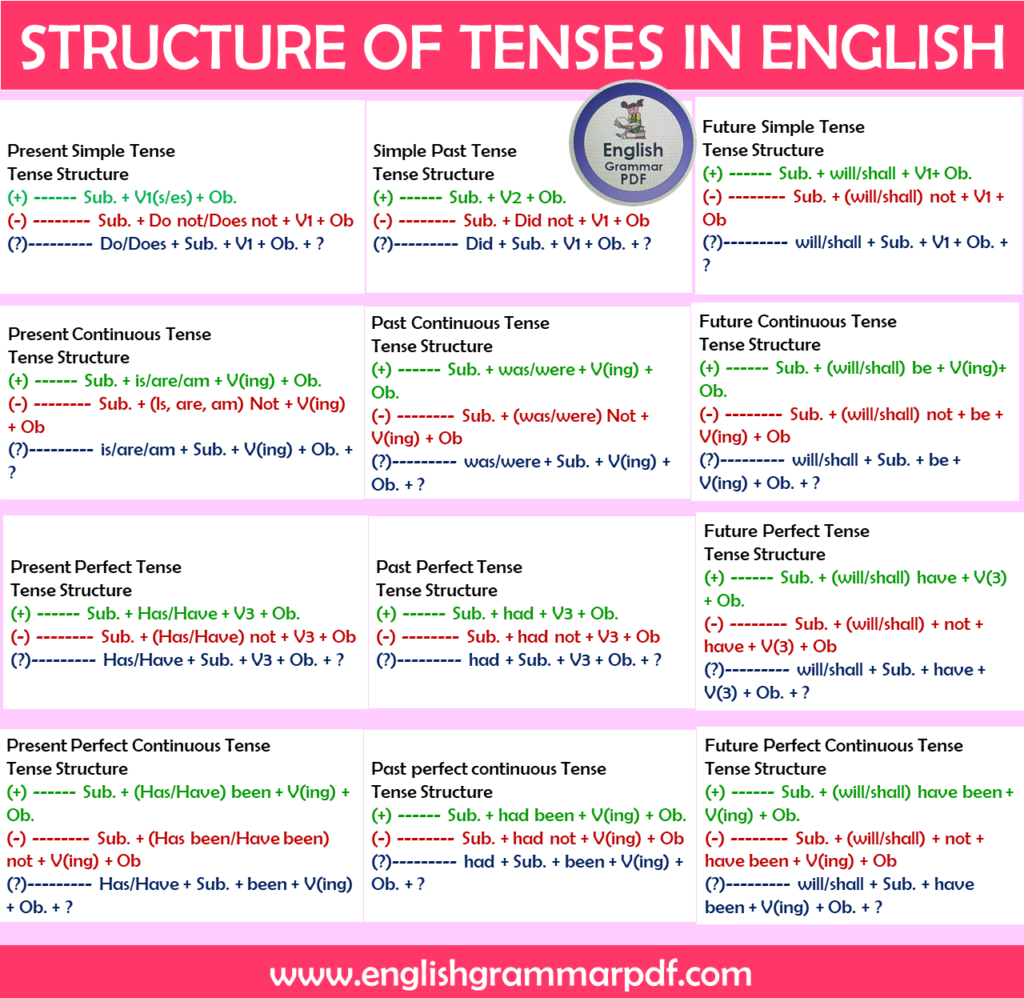
The English language has 12 main verb tenses. Each tense is used to express specific times and actions or states. These tenses are divided into three main categories: past, present, and future, and each category has four aspects: simple, continuous (also known as progressive), perfect, and perfect continuous. Here are the 12 types of tenses:
- Present Simple
- Present Continuous (Progressive)
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous (Progressive)
- Past Simple
- Past Continuous (Progressive)
- Past Perfect
- Past Perfect Continuous (Progressive)
- Future Simple
- Future Continuous (Progressive)
- Future Perfect
- Future Perfect Continuous (Progressive)
1- Present Indefinite Tense
The present tense is used to express an action that is happening now.
Formation and Examples:
Affirmative: (Subject+verb+Object)
Examples:
- She reads a book every night.
- They play soccer on Saturdays.
- The sun rises in the east.
- He speaks four languages.
- Cats love to sleep during the day.
Negative: Subject+Does not+verb+ Object
Examples:
- She does not read a book every night.
- They do not play soccer on Saturdays.
- The sun does not rise in the west.
- He does not speak four languages.
- Cats do not love to swim.
Interrogative: Do+Subject+verb+ Object?
Examples:
- Does she read a book every night?
- Do they play soccer on Saturdays?
- Does the sun rise in the east?
- Does he speak four languages?
- Do cats love to sleep during the day?
2- Present Continuous Tense
The present continuous tense is used to express an action that is happening now and will continue for some time.
Formation and Examples:
Affirmative: (Subject+is/am/are+verb+ing) + Object
Examples:
- She is reading a book now.
- They are playing soccer at the moment.
- The sun is shining brightly.
- He is learning Spanish.
- The baby is sleeping.
Negative: Subject+Is/Am/Are not +verb+ing+ Object
Examples:
- She is not reading a book now.
- They are not playing soccer at the moment.
- The sun is not shining brightly.
- He is not learning Spanish.
- The baby is not sleeping.
Interrogative: Is/Am/Are+Subject+verb+ing + Object?
Examples:
- Is she reading a book now?
- Are they playing soccer at the moment?
- Is the sun shining brightly?
- Is he learning Spanish?
- Is the baby sleeping?
3- Present Perfect Tense
The present perfect tense is used to express an action that has already happened.
Formation and Examples:
Affirmative: (Subject+has/have+Object) + verb+ed
Examples:
- She has finished her homework.
- They have visited Paris.
- He has written a novel.
- I have lost my keys.
- We have eaten dinner.
Negative: Subject+has/have not+Object+verb+ed
Examples:
- She has not finished her homework.
- They have not visited Paris.
- He has not written a novel.
- I have not lost my keys.
- We have not eaten dinner.
Interrogative: Has/Have+Subject+object+verb+ed?
Examples:
- Has she finished her homework?
- Have they visited Paris?
- Has he written a novel?
- Have I lost my keys?
- Have we eaten dinner?
4- Present Perfect Continuous Tense
The present perfect continuous tense is used to express an action that has already happened and will continue for some time.
Formation and Examples:
Affirmative: (Subject+has/have been+verb+ing) + Object
Examples:
- She has been reading for two hours.
- They have been playing since morning.
- He has been working on the project for a week.
- I have been learning Spanish for a year.
- We have been waiting here for thirty minutes.
Negative: Subject+has/have not been+verb+ing + Object
Examples:
- She has not been reading for two hours.
- They have not been playing since morning.
- He has not been working on the project for a week.
- I have not been learning Spanish for a year.
- We have not been waiting here for thirty minutes.
Interrogative: Has/Have+Subject+been verb+ing + Object?
Examples:
- Has she been reading for two hours?
- Have they been playing since morning?
- Has he been working on the project for a week?
- Have I been learning Spanish for a year?
- Have we been waiting here for thirty minutes?
5- Past Indefinite Tense
The simple past tense is used to express an action that has happened in the past.
Formation and Examples:
Affirmative: (Subject+object+verb+ed)
Examples:
- She read a book last night.
- They played soccer yesterday.
- The sun set at 6 PM yesterday.
- He spoke to me last week.
- The dog barked loudly.
Negative: Subject+Object+didn’t/did not + verb+ed
Examples:
- She did not read a book last night.
- They did not play soccer yesterday.
- The sun did not set at 8 PM.
- He did not speak to me last week.
- The dog did not bark loudly.
Interrogative: Did/Did+Subject+object+verb+ed?
Examples:
- Did she read a book last night?
- Did they play soccer yesterday?
- Did the sun set at 6 PM yesterday?
- Did he speak to me last week?
- Did the dog bark loudly?
6- Past Continuous Tense
The past continuous tense is used to express an action that was in progress at some point of time.
Formation and Examples:
Affirmative: (Subject+was/were+verb+ing) + Object
Examples:
- She was reading a book when I called.
- They were playing soccer at 5 PM yesterday.
- The sun was setting as we left.
- He was speaking loudly in the meeting.
- The children were playing in the park.
Negative: Subject+was/were not+verb+ing + Object
Examples:
- She was not reading a book when I called.
- They were not playing soccer at 5 PM yesterday.
- The sun was not setting as we left.
- He was not speaking loudly in the meeting.
- The children were not playing in the park.
Interrogative: Was/Were+Subject+verb+ing+Object?
Examples:
- Was she reading a book when you called?
- Were they playing soccer at 5 PM yesterday?
- Was the sun setting as you left?
- Was he speaking loudly in the meeting?
- Were the children playing in the park?
7- Past Perfect Tense
The past perfect tense is used to express an action that happened before some other event in the past.
Formation and Examples:
Affirmative: Subject+had+object+verb+ed)
Examples:
- She had finished her homework before going to bed.
- They had visited Paris before moving to London.
- He had written a novel by the end of last year.
- I had lost my keys before I found them in my bag.
- We had eaten dinner before the guests arrived.
Negative: Subject+had not + Object + verb+ed)
Examples:
- She had not finished her homework before going to bed.
- They had not visited Paris before moving to London.
- He had not written a novel by the end of last year.
- I had not lost my keys before I found them in my bag.
- We had not eaten dinner before the guests arrived.
Interrogative: Had+Subject+object+verb+ed?
Examples:
- Had she finished her homework before going to bed?
- Had they visited Paris before moving to London?
- Had he written a novel by the end of last year?
- Had I lost my keys before finding them?
- Had we eaten dinner before the guests arrived?
8- Past Perfect Continuous Tense
The past perfect continuous tense is used to express an action that had been going on for some time before another action in the past took place.
Formation and Examples:
Affirmative: (Subject+had been+verb+ing)+Object
Examples:
- She had been reading for two hours before I arrived.
- They had been playing football all afternoon when it started to rain.
- He had been working on the project for several months before it was completed.
- I had been learning Spanish for two years before moving to Spain.
- We had been waiting for the bus for an hour when it finally came.
Negative: Subject+had not+been+verb+ing + Object
Examples:
- She had not been reading for two hours before I arrived.
- They had not been playing football all afternoon when it started to rain.
- He had not been working on the project for several months before it was completed.
- I had not been learning Spanish for two years before moving to Spain.
- We had not been waiting for the bus for an hour when it finally came.
Interrogative: Had+Subject+been+verb+ing?
Examples:
- Had she been reading for two hours before you arrived?
- Had they been playing football all afternoon when it started to rain?
- Had he been working on the project for several months before it was completed?
- Had I been learning Spanish for two years before moving to Spain?
- Had you been waiting for the bus for an hour when it finally came?
9- Future Indefinite Tense
The future indefinite tense is used to express an action that will take place in the future.
Formation and Examples:
Affirmative: Subject+will/shall+verb+Object
Examples:
- She will visit her grandparents next weekend.
- They will start a new project soon.
- He will buy a new car next month.
- I will travel to Japan next year.
- We will have dinner at 8 PM.
Negative: Subject+will not + Object + verb
Examples:
- She will not visit her grandparents next weekend.
- They will not start a new project soon.
- He will not buy a new car next month.
- I will not travel to Japan next year.
- We will not have dinner at 8 PM.
Interrogative: Will/shall+Subject+verb?
Examples:
- Will she visit her grandparents next weekend?
- Will they start a new project soon?
- Will he buy a new car next month?
- Will I travel to Japan next year?
- Will we have dinner at 8 PM?
10- Future Continuous Tense
The future continuous tense is used to express an action that will be taking place in the future.
Formation and Examples:
Affirmative: Subject+will/shall+be+verb+ing+Object
Examples:
- She will be studying all night.
- They will be playing basketball tomorrow afternoon.
- He will be working on the project next week.
- I will be traveling during the summer.
- We will be having a meeting at this time tomorrow.
Negative: Subject+will not+be+verb+ing + Object
Examples:
- She will not be studying all night.
- They will not be playing basketball tomorrow afternoon.
- He will not be working on the project next week.
- I will not be traveling during the summer.
- We will not be having a meeting at this time tomorrow.
Interrogative: Will/shall+Subject+be+verb+ing?
Examples:
- Will she be studying all night?
- Will they be playing basketball tomorrow afternoon?
- Will he be working on the project next week?
- Will I be traveling during the summer?
- Will we be having a meeting at this time tomorrow?
11- Future Perfect tense
The future perfect tense is used to express an action that will have taken place in the future.
Formation and Examples:
Affirmative: Subject+will/shall+have+verb+Object
Examples:
- She will have finished her assignment by tomorrow.
- They will have built the house by next year.
- He will have completed the course by next month.
- I will have saved enough money by the end of the year.
- We will have arrived at the destination by noon.
Negative: Subject+will not+have+verb+Object
Examples:
- She will not have finished her assignment by tomorrow.
- They will not have built the house by next year.
- He will not have completed the course by next month.
- I will not have saved enough money by the end of the year.
- We will not have arrived at the destination by noon.
Interrogative: Will/shall+Subject+have+verb?
Examples:
- Will she have finished her assignment by tomorrow?
- Will they have built the house by next year?
- Will he have completed the course by next month?
- Will I have saved enough money by the end of the year?
- Will we have arrived at the destination by noon?
12- Future Perfect Continuous Tense
The future perfect continuous tense is used to express an action that will have been taking place in the future for a period of time.
Formation and Examples:
Affirmative: Subject+will/shall+have+been+verb+ing)+Object
Examples:
- She will have been studying for three hours by the time we arrive.
- They will have been working on the project for six months by its completion.
- He will have been running for an hour by the time he finishes.
- I will have been learning Spanish for two years by the time I visit Spain.
- We will have been waiting for thirty minutes by the time the show starts.
Negative: Subject+will not+have+been+verb+ing)+Object
Examples:
- She will not have been studying for three hours by the time we arrive.
- They will not have been working on the project for six months by its completion.
- He will not have been running for an hour by the time he finishes.
- I will not have been learning Spanish for two years by the time I visit Spain.
- We will not have been waiting for thirty minutes by the time the show starts.
Interrogative: Will/shall+Subject+have+been+verb+ing?
Examples:
- Will she have been studying for three hours by the time we arrive?
- Will they have been working on the project for six months by its completion?
- Will he have been running for an hour by the time he finishes?
- Will I have been learning Spanish for two years by the time I visit Spain?
- Will we have been waiting for thirty minutes by the time the show starts?