Types of Conjunctions in English grammar with Pdf. The conjunction is explained with definition and examples. All the kinds of conjunction are explained with definitions and examples. After learning all these types you will never mistake related conjunction. It is very useful lesson. You can Download PDF of this lesson.
Types of conjunctions in English grammar with PDF
What is conjunction?
A word that is used to join two other words, two clauses, or two sentences is known as conjunction. Some common conjunctions are and, but, still, either, neither and yet etc.
Use of conjunctions in daily used sentences.
Both she and her mother are beautiful.
Work hard otherwise you will fail.
She was ill; so she will not go to school.
Here you will learn all types of conjunction in English grammar with PDF.
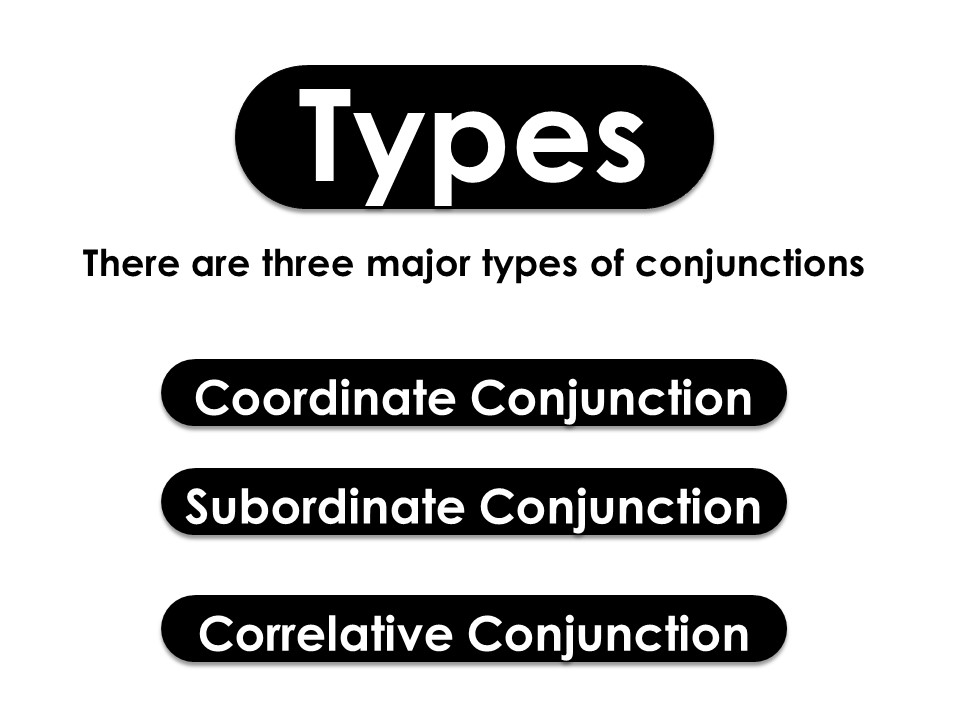
What are different types of conjunction?
There are two major types of conjunction.
- Coordinating conjunctions
- Subordinating Conjunctions
- Corelative conjunctions
1. Coordinating Conjunctions
They join sentences of of coordinate (of equal) rank.
- He came here and met me.
- He came to see me but I was not at home.
List of some important coordinating conjunctions is;
And, both, also, to, as well as, no less than, not only, but, now, well, either, or, neither, nor, otherwise, else, but, still, yet, nevertheless, however, whereas, while, only, therefore, then, so then, for etc.
Types of Coordinating Conjunctions
The coordinating conjunctions are further divided into following types.
- Cumulative or Compulative conjunctions
- Disjunctive or Alternative conjunctions
- The adversative conjunctions
- The illative conjunctions
Cumulative or Compulative conjunctions
They join two independent clauses of the same type. Examples of cumulative or commpulative clauses are ; and, both, also, too, as well as, no less than, not only, but also etc.
Both he and his brother are intelligent.
Not only I but also my father went there.
Disjunctive or alternative conjunctions
They combine two independent clauses denoting choice between two things. Example of disjunctive or alternative conjunctions are; or, either, neither else, otherwise, either-or, neither-nor etc.
Work hard, otherwise you will fail.
Either he or his brother has stolen my pen.
The adversative conjunctions
They combine independent clause of the opposite type. Some examples of the adversative conjunctions are; still, however, whereas, only, while, nevertheless, but, yet etc.
He is poor, but he is honest.
He was ill, still he did his duty.
The illative conjunctions
They combine two independent clauses denoting effect or inference. Some common examples of the illative conjunctions are; so, hence, thus, therefore, because, as, for, etc.
He was ill; so he did not go to school.
It was very hot therefore we stopped our journey.
2. Subordinating conjunctions
They join a subordinating or dependent clause to a principal clause (of higher rank).
I will read that book if you advise me.
Principal: I will read that book
Conjunction: if
Dependent: you advise me
List of important subordinating conjunctions is; that, because so that, if, unless, as if, whether, though, however, not withstanding, as-as, as much as, no less than, as for as, according as, while, as soon as, after, since, so long as etc.
Subordinating conjunctions normally performs.
- Cause or reason
- Purpose
- Condition
- Contrast
- Comparison
- Time or period
- Effect
- Manner
- Apposition
- Concession
3.Correlative conjunction
Such conjunction are pairs of words that work together to connect parts of a sentence that have equal value. If there is not a pair of words working together, a different type of conjunction is being used.
A Power List of Conjunctions
| Also | And | Another |
| In the same manner | In the same way | Just as important |
| Ultimately | What | Whatever |
| As soon as | At last | At lenght |
| Lastly | Later | Meanwhile |
| When | While | With this in mind |
| Consequently | Conversely | Equally important |
| Of equal importance | On the contrary | On the following day |
| Yet | ||
| Because | Because of this | Before |
| Moreover | Nevertheless | Next |
| However | In addition | In conclusion |
| The next week | Then | Thereafter |
| Besides | Briefly | But |
| Nonetheless | Now | Nor |
| A minute later | Accordingly | Actually |
| In spite of | In spite of this | In summary |
| To be specific | To begin with | To illustrate |
| For instance | For this purpose | For this reason |
| Presently | Second | Similarly |
| Furthermore | Gradually | Hence |
| Still | Subsequently | Such as |
| Finally | First | For example |
| On the other hand | Other hand | Or |
| In contrast | In fact | In short |
| Therefore | Third | Thus |
| Fourth | From here on | Further |
| Since | So | Soon |
| As an example | As a consequence | As a result |
| Least | Last | Last of all |
| Whoever | Whereas | Whomever |
| After | After a short time | Afterwards |
| In the end | In the meanwhile | In the meantime |
| To repeat | To sum up | Too |
You can download the types of conjunctions in English grammar pdf.