Garden vocabulary is very important for farmers and the one with the hobby of gardening. While taking about garden and working in garden you might think that what the English word is for specific thing. This is a list of 100 gardening vocabulary words, complete with easy-to-understand meanings.
This collection is designed to enrich your gardening knowledge in a simple and accessible way. Whether you’re a budding green thumb or an experienced gardener, this list will be your handy reference, making your gardening experience more enjoyable and successful. Let’s explore the Garden words!
Gardening Vocabulary Words
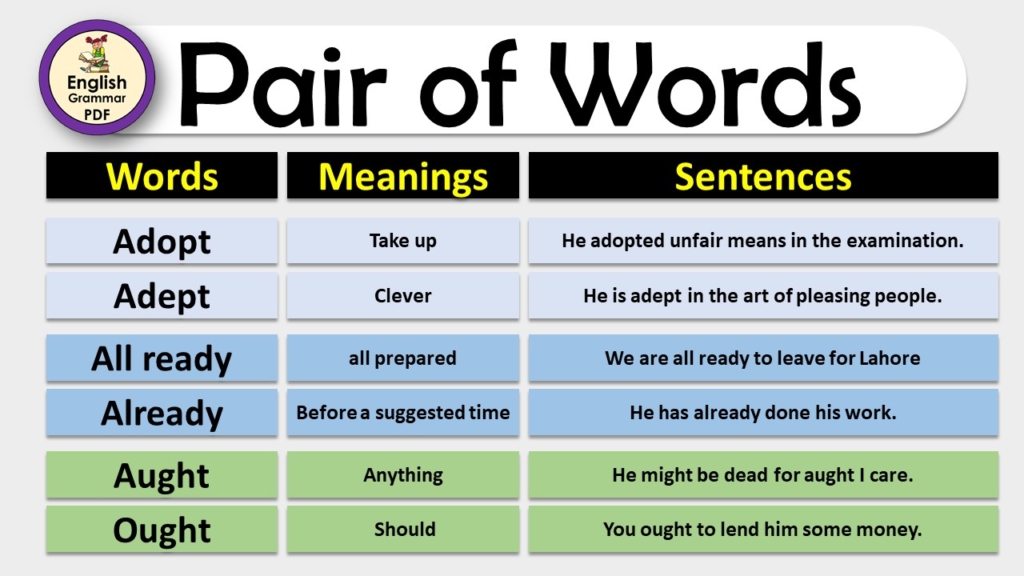
- Potting: Placing plants in a container.
- Soil: The top layer of earth where plants grow.
- Seed: A plant’s unit of reproduction.
- Watering: Applying water to plant soil.
- Mulch: Material spread over soil for protection.
- Compost: Decomposed organic matter enriching soil.
- Pruning: Cutting back plants to shape them.
- Weeding: Removing unwanted plants from soil.
- Fertilizer: Substance added to soil to nourish plants.
- Sunlight: Natural light from the sun.
- Shade: Area sheltered from direct sunlight.
- Transplanting: Moving a plant to another location.
- Evergreen: Plants keeping leaves year-round.
- Hardiness: Plant’s ability to withstand cold.
- Aeration: Introducing air into soil.
- Grafting: Joining two plants together.
- Cultivar: Plant variety bred for traits.
- Hybrid: Offspring from two different plants.
- Propagation: Creating new plants from existing ones.
- Herbicide: Chemical that kills unwanted plants.
- Tilling: Turning over soil to prepare it.
- Soil Amendment: Adding materials to improve soil.
- pH Level: Measure of soil acidity/alkalinity.
- Trowel: Small hand tool for digging.
- Rake: Tool for gathering or smoothing soil.
- Hoe: Long-handled tool for cultivating soil.
- Shovel: Tool for digging or moving material.
- Wheelbarrow: One-wheeled cart for transporting materials.
- Gloves: Protective hand covering for gardening.
- Shears: Large scissors for trimming plants.
- Secateurs: Handheld pruners for cutting branches.
- Tiller: Tool or machine for breaking soil.
- Trellis: Framework supporting climbing plants.
- Irrigation: Supplying water to plants systematically.
- Pesticide: Chemical for killing plant pests.
- Organic: Derived from living matter.
- Perennial: Plant living more than two years.
- Annual: Plant living only one year.
- Biennial: Plant with a two-year lifecycle.
- Bulb: Underground plant storage organ.
- Root: Part of plant anchoring it underground.
- Stem: Plant’s main aboveground stalk.
- Leaves: Plant’s main photosynthetic organs.
- Deciduous: Trees/shrubs losing leaves annually.
- Germination: Process of seed developing into plant.
- Humus: Organic component of soil.
- Loam: Soil with balanced sand, silt, clay.
- Sand: Coarse, granular soil component.
- Silt: Fine, fertile soil particles.
- Clay: Fine-grained, nutrient-rich soil.
- Inorganic: Not consisting of living matter.
- Drought Tolerance: Ability to withstand dry conditions.
- Rootstock: Root part of grafted plant.
- Scion: Upper part of grafted plant.
- Budding: New growth on a plant.
- Layering: Rooting branches while attached to parent.
- Pollination: Transfer of pollen to enable fertilization.
- Cross-Pollination: Pollen transfer between different plants.
- Deadheading: Removing spent flowers.
- Thinning: Removing excess plants for growth.
- Vermiculture: Using worms to decompose organic waste.
- Hydroponics: Growing plants in water without soil.
- Aquaponics: Combining fish farming with hydroponics.
- Greenhouse: Structure for growing plants in controlled conditions.
- Cold Frame: Small outdoor structure to protect plants.
- Horticulture: Art and science of garden cultivation.
- Botany: Scientific study of plants.
- Permaculture: Sustainable and self-sufficient agricultural ecosystem.
- Xeriscaping: Landscaping to reduce water usage.
- Espalier: Training trees or shrubs on a flat plane.
- Arboretum: Botanical garden specializing in trees.
- Bonsai: Art of growing miniature trees.
- Topiary: Art of clipping plants into ornate shapes.
- Vermiculite: Mineral used in soil conditioning.
- Perlite: Volcanic glass for aerating soil.
- Peat Moss: Decayed vegetable matter for soil.
- Compost Tea: Liquid made from steeped compost.
- Biochar: Charcoal used as a soil amendment.
- Mulching: Applying material to soil surface.
- Cover Crop: Plant grown to improve soil health.
- Crop Rotation: Growing different crops sequentially.
- Nematode: Microscopic worms, some harmful to plants.
- Mycorrhiza: Fungus that forms symbiotic relationships with plants.
- Aeroponics: Growing plants in an air/mist environment.
- Seedling: Young plant grown from seed.
- Sapling: Young tree.
- Graft Union: Junction where grafting is done.
- Node: Point on a stem where leaves attach.
- Internode: Stem segment between two nodes.
- Variegation: Different colored zones in plant leaves.
- Chlorosis: Yellowing of leaves due to lack of chlorophyll.
- Blight: Disease causing plant wilting and death.
- Mildew: Fungal disease affecting plants.
- Mosaic: Virus causing mottled coloring on leaves.
- Rust: Fungal disease forming orange-brown spots.
- Scorch: Leaf damage from too much light/heat.
- Spore: Reproductive cell in some plants and fungi.
- Stolon: Aboveground shoot that roots to form new plants.
- Rhizome: Underground stem for storage and new growth.
- Corm: Short, vertical, swollen underground plant stem.
- Tuber: Thickened underground part of a stem.
- Drip Line: Ground area under the outer leaves of a tree.
- Canopy: Upper layer of trees or plants.
- Bract: Modified leaf associated with a flower or inflorescence.
- Petiole: Stalk that attaches a leaf blade to stem.
- Sepal: Outer parts of the flower, typically green.
- Pistil: Female reproductive part of a flower.
- Stamen: Male reproductive organ in flowers.
- Pollinator: Animal that moves pollen from flower to flower.
- Inflorescence: Group or cluster of flowers arranged on a stem.
- Panicle: Loose, branching flower cluster.
- Raceme: Simple inflorescence with stalked flowers along a central stem.
- Umbel: Flower cluster with stems all of equal length.
- Cyme: Flat-topped or rounded flower cluster.
- Alkalinity: Measure of the soil’s capacity to neutralize acid.
- Acidic Soil: Soil with a pH less than 7.
- Soil Texture: Relative proportion of sand, silt, and clay in soil.
Explore More:
Basic English Vocabulary Words
Daily Use English Words With Meanings
Wedding Vocabulary | Negative Words List | Positive Words List

Download this lesson in PDF