When it comes to English grammar, understanding the difference between “like” and “as” can be crucial for clear and correct communication. Both words can be used to make comparisons, but they are not interchangeable.
Each serves its unique function within a sentence, and confusing them can lead to unclear or incorrect statements. In this post, we’ll explore the distinctions between “like” and “as,” offering examples to help you master their usage.
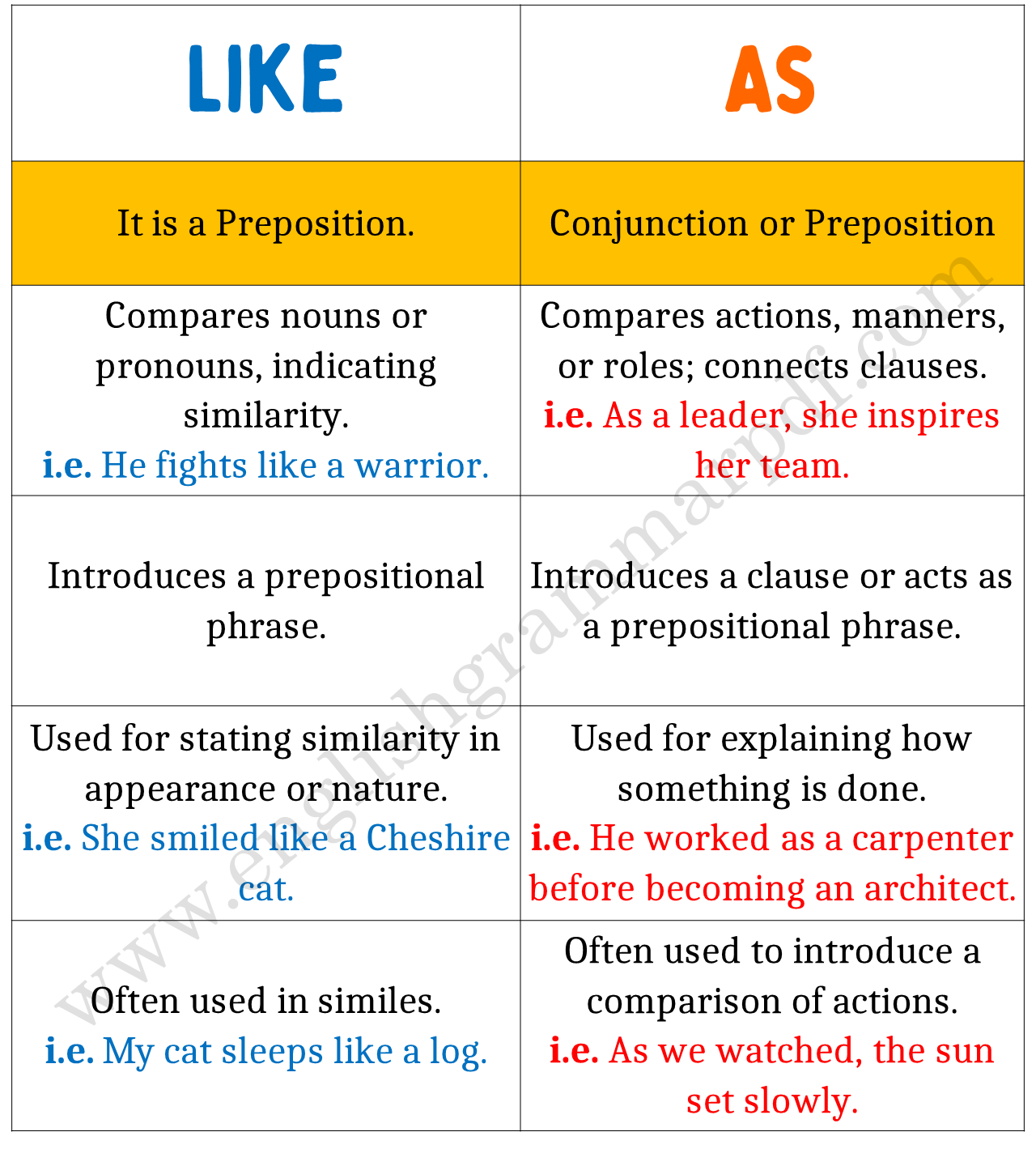
Understanding “Like”
“Like” is a preposition that is used to compare similar things or to say that things are similar in appearance, nature, or form. When using “like,” the comparison involves looking at one thing and noting its resemblance to another. It often introduces a prepositional phrase.
Examples of “like”:
- She sings like an angel. (Comparison of the way she sings to the way an angel would sing, hypothetically.)
- He runs like the wind. (Comparison of his speed to the wind.)
Understanding “As”
“As” can function as a conjunction or a preposition, but its role as a conjunction is where most confusion with “like” occurs. When used as a conjunction, “as” is involved in comparing actions or the manner in which actions are carried out. It connects two clauses, indicating that something happens in the same manner or at the same time as something else.
Examples of “as” (conjunction):
- As I arrived, the rain started to fall. (Indicates that the arrival and the beginning of the rain happened simultaneously.)
- She left the room as quietly as she had entered. (Comparison of the manner of leaving with the manner of entering.)
Key Differences
Grammatical Function:
- “Like” is used as a preposition to introduce a prepositional phrase.
- “As” can be used both as a preposition and a conjunction, but its use as a conjunction to compare actions is the critical difference.
Type of Comparison:
- “Like” compares nouns or pronouns, implying similarity.
- “As” compares actions or entire clauses, emphasizing the manner or timing of an action.
Contextual Usage:
- Use “like” when stating that something is similar to something else.
- Use “as” when discussing how something is done or when two actions correlate.
Examples to Clarify
- Correct: He acts like a clown. (Comparison of his actions to those of a clown.)
- Incorrect: He acts as a clown. (This suggests he is substituting as a clown, which is not the intended meaning unless he really is performing as a clown.)
- Correct: As the president, he must be cautious. (Describes his role and the associated behavior.)
- Incorrect: Like the president, he must be cautious. (This would imply he is not the president but needs to be cautious in a similar way, which changes the meaning.)