Adverbs play a crucial role in enhancing our understanding of how, where, and when an action takes place. In English grammar, the order in which adverbs appear within a sentence can significantly impact the clarity and correctness of our communication.
This post delves into the basics of adverbs and the commonly accepted order in which they should appear in sentences—specifically focusing on the sequence of adverbs of manner, place, and time.
Definition of Adverbs
An adverb is a word that modifies or qualifies verbs, adjectives, other adverbs, or whole sentences.
It provides additional information about the manner, place, time, frequency, certainty, or degree of the action or condition.
Adverbs often end in “-ly” but not always (e.g., fast, well, very, now, too).
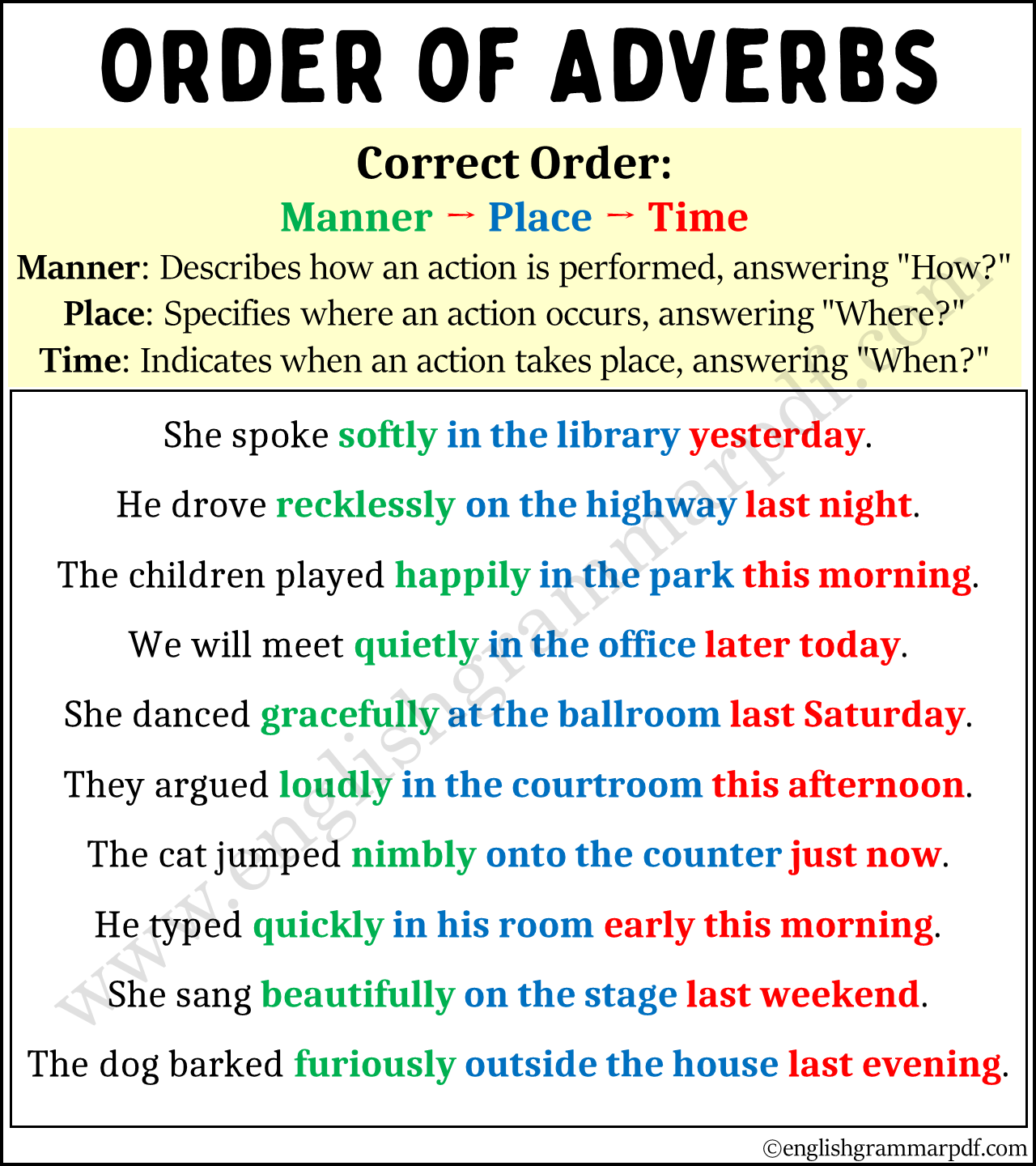
Order of Adverbs:
Correct Order: Manner – Place – Time
When you have to use adverbs of manner, place, and time in the same sentence, the general guideline is to arrange them in that exact order: Manner, Place, and then Time. This order is preferred because it usually makes the sentence clearer and easier to understand.
Correct: “She danced gracefully in the ballroom all night.”
- Manner: gracefully – How did she dance?
- Place: in the ballroom – Where did she dance?
- Time: all night – When did she dance?
Incorrect: “She danced all night gracefully in the ballroom.”
- This arrangement is less common and can sound awkward or confusing.
1. Adverb of Manner
This type of adverb describes how an action is performed. It answers the question “in what manner?” or “how?” Common adverbs of manner include slowly, quickly, well, badly, and silently.
For example:
- She sings beautifully.
- The baby slept soundly.
2. Adverb of Place
Adverbs of place specify where the action of the verb is happening. They answer the question “where?” Examples include here, there, everywhere, outside, and upstairs.
For instance:
- He looked everywhere for his keys.
- They usually play basketball outside.
3. Adverb of Time
Adverbs of time provide information about when an action occurred. They answer “when?” This includes soon, now, then, early, and yesterday.
For example:
- We will start the meeting soon.
- She finished her work early.