Understanding time conjunctions is essential for constructing clear and coherent sentences in English. These conjunctions help us link events with specific timing, making our speech and writing more fluid and precise. In this post, we’ll explore various time conjunctions, define each, and provide practical examples to help you use them effectively in your daily communication.
List of Time Conjunctions
Here is the list of all time conjunctions in English:
- Before
- After
- When
- While
- Until
- Since
- As soon as
- Once
- Whenever
- By the time
Time Conjunctions in English
Before
“Before” is a conjunction used to indicate that one event occurs earlier than another. It sets the stage for a sequence where the action in the main clause is preceded by the action in the subordinate clause. This conjunction is versatile, functioning in various contexts to establish a clear timeline.
Examples
- Finish your homework before you watch TV.
- She had left before I arrived.
- Make sure to call me before you leave the house.
- The birds flew away before we could take a picture.
- He always brushes his teeth before he goes to bed.
- Please submit the report before the deadline next Friday.
- She had completed the project before the semester ended.
- He had eaten before he came to the party.
- The concert had ended before the rain started.
- Lock the door before you go out.
After
“After” is used to show that an event occurs subsequent to a point in time or another event. It highlights the sequence where the main clause action follows the time or event mentioned in the subordinate clause.
Examples
- We went for a walk after dinner.
- She will call you after she finishes her meeting.
- The children went to bed after the movie ended.
- He started feeling better after he took the medicine.
- She decided to go to the gym after dropping her kids at school.
- The team celebrated after winning the championship.
- He read the book after he saw the movie.
- They moved to a new house after they got married.
- The store will reopen after the renovation is complete.
- She started her own business after retiring.
When
“When” is used to introduce a clause where the timing of one action coincides with another. It links events that happen at the same time, expressing a relationship of timing between two actions.
Examples
- I was watching TV when the phone rang.
- When you see her, tell her to call me.
- He was leaving when I arrived.
- When the clock strikes twelve, the show will start.
- She was singing when he walked in.
- We were just talking about you when you called.
- When I wake up, I always drink coffee.
- They were playing games when it started to rain.
- He was not paying attention when the teacher asked him a question.
- When summer arrives, we go to the beach.
While
“While” indicates that two or more actions or events occur simultaneously. It emphasizes the duration of an action in the background of another ongoing action.
Examples
- She reads while he watches TV.
- I listen to podcasts while I work out.
- They were talking while walking to school.
- He injured his ankle while playing soccer.
- Please be quiet while the baby is sleeping.
- She found her keys while she was cleaning the house.
- While I was cooking, the phone rang.
- He likes to listen to music while studying.
- They received the news while having dinner.
- Keep stirring the sauce while it cooks.
Until
“Until” conveys that an action continues up to a certain point in time and then stops. It is used to mark the duration leading up to a specific moment or event.
Examples
- Keep stirring until the mixture thickens.
- She waited until he returned.
- We played games until midnight.
- The shop is open until 9 PM.
- He didn’t leave until the meeting was over.
- She didn’t know about the surprise until her birthday.
- I cannot relax until all the work is done.
- They will be staying with us until the end of the month.
- Study until you feel prepared for the exam.
- The lights stayed on until dawn.
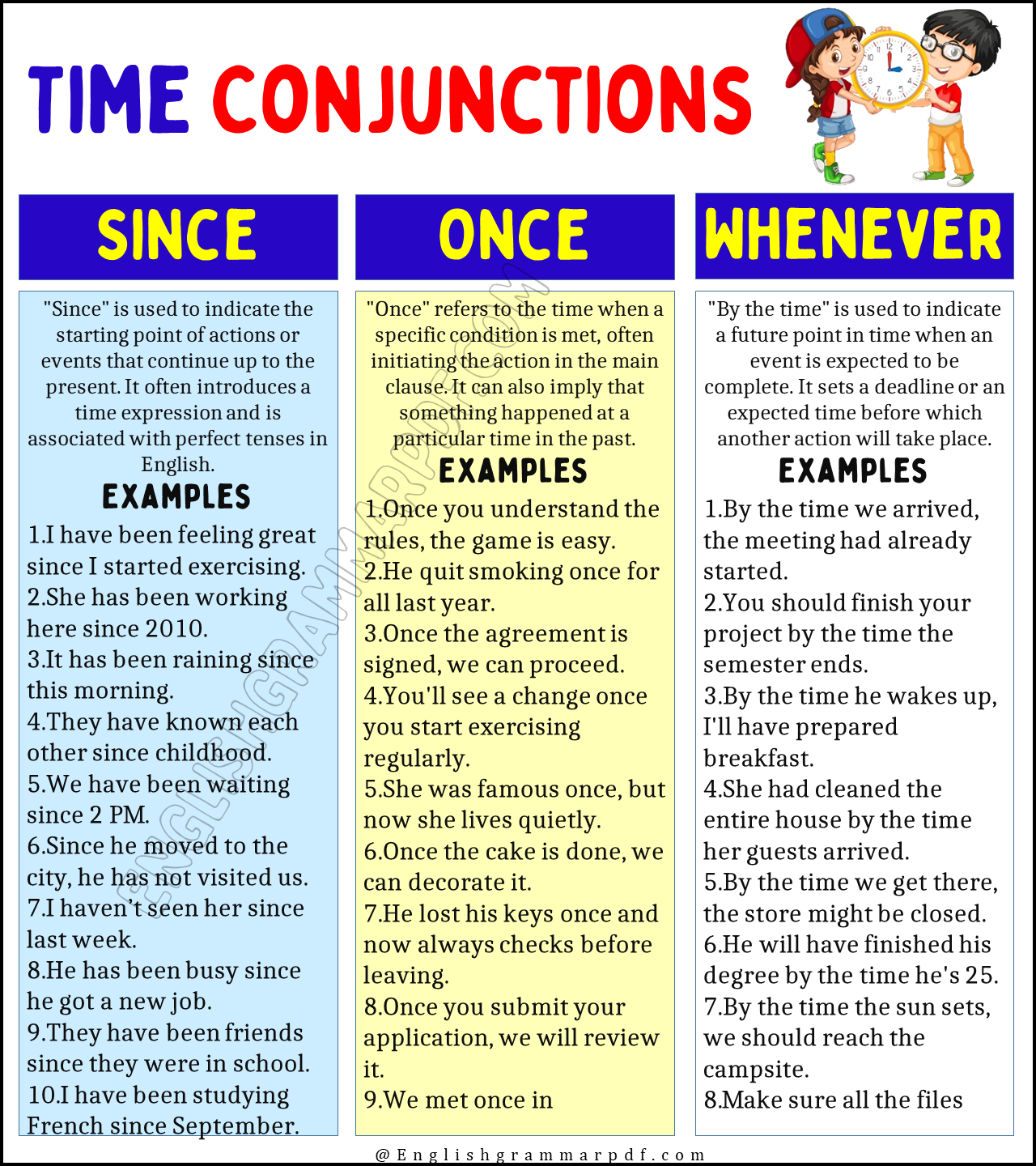
Since
“Since” is used to indicate the starting point of actions or events that continue up to the present. It often introduces a time expression and is associated with perfect tenses in English.
Examples
- I have been feeling great since I started exercising.
- She has been working here since 2010.
- It has been raining since this morning.
- They have known each other since childhood.
- We have been waiting since 2 PM.
- Since he moved to the city, he has not visited us.
- I haven’t seen her since last week.
- He has been busy since he got a new job.
- They have been friends since they were in school.
- I have been studying French since September.
As soon as
“As soon as” implies immediacy, indicating that one event follows another without delay. It stresses the minimal gap between two consecutive actions.
Examples
- Call me as soon as you arrive.
- She will send you the information as soon as she receives it.
- As soon as the bell rings, please proceed to the assembly.
- He started working as soon as he finished his breakfast.
- As soon as the doors opened, the crowd rushed in.
- They left as soon as the concert was over.
- Please reply as soon as possible.
- As soon as he gets the approval, he will start the project.
- The game was canceled as soon as it started raining.
- She apologized as soon as she realized her mistake.
Once
“Once” refers to the time when a specific condition is met, often initiating the action in the main clause. It can also imply that something happened at a particular time in the past.
Examples
- Once you understand the rules, the game is easy.
- He quit smoking once for all last year.
- Once the agreement is signed, we can proceed.
- You’ll see a change once you start exercising regularly.
- She was famous once, but now she lives quietly.
- Once the cake is done, we can decorate it.
- He lost his keys once and now always checks before leaving.
- Once you submit your application, we will review it.
- We met once in a conference last year.
- Once the rain stops, we can go out.
Whenever
“Whenever” introduces a condition that can happen at any unspecified time or multiple times. It is used to indicate flexibility in the timing of an action.
Examples
- You can call me whenever you need help.
- Whenever it rains, the traffic becomes terrible.
- She visits her parents whenever she has a few days off.
- He takes a walk whenever he takes a break from work.
- Whenever I cook, I like to try new recipes.
- You can start whenever you’re ready.
- They go skiing whenever they get the chance.
- She buys books whenever she goes shopping.
- Whenever the phone rings, the dog barks.
- He watches movies whenever he feels stressed.
By the time
“By the time” is used to indicate a future point in time when an event is expected to be complete. It sets a deadline or an expected time before which another action will take place.
Examples
- By the time we arrived, the meeting had already started.
- You should finish your project by the time the semester ends.
- By the time he wakes up, I’ll have prepared breakfast.
- She had cleaned the entire house by the time her guests arrived.
- By the time we get there, the store might be closed.
- He will have finished his degree by the time he’s 25.
- By the time the sun sets, we should reach the campsite.
- Make sure all the files are uploaded by the time I check them.
- By the time the concert begins, we should secure a good spot.
- The flowers will bloom by the time spring arrives.